The Invisible Force: How to Make Static Electricity Dance with Just a Balloon!
Hi, I’m Ken Kuwako, your Science Trainer. Every day is an experiment!
That mysterious “snap” and “crackle” when you take off your sweater on a cold winter day. The way your hair stands up poof! after rubbing it with a plastic ruler. Everyone has experienced these things, right? These phenomena, which seem almost like magic, are actually caused by an invisible, tiny force called static electricity.
Today, I’m going to introduce a super simple experiment that will help you “visualize” the power of static electricity that surrounds us every day. Just by hanging a balloon from the ceiling, you can clearly see the effects of static electricity’s force. Now, let’s use the video below as a hint and uncover the true nature of this scientific magic together!
Through this experiment, you will explore the forces acting on the balloon and the conditions under which this phenomenon occurs. By doing so, you’ll gain an incredibly clear understanding of how static electricity works. Now, let the adventure into the world of electric charge begin!
What You’ll Need
Two Balloons
String
A Handkerchief or Towel (A dry material like wool or silk is recommended)
The Experiment (Step-by-Step)
1 Inflate one balloon and hang it from the ceiling with a string. It should be able to swing freely.
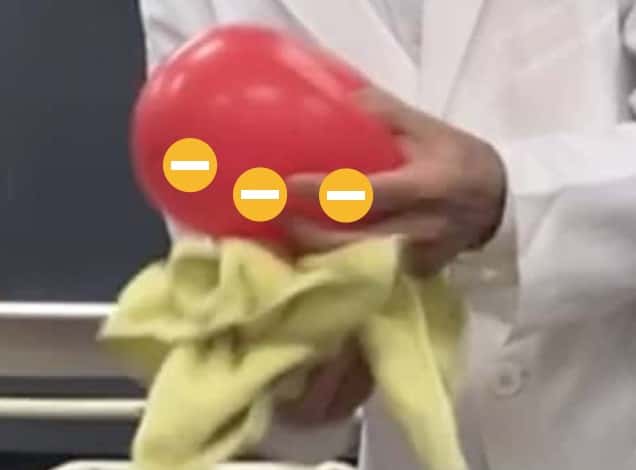
2 Rub the hanging balloon vigorously with the handkerchief about 10 times, moving in one direction.
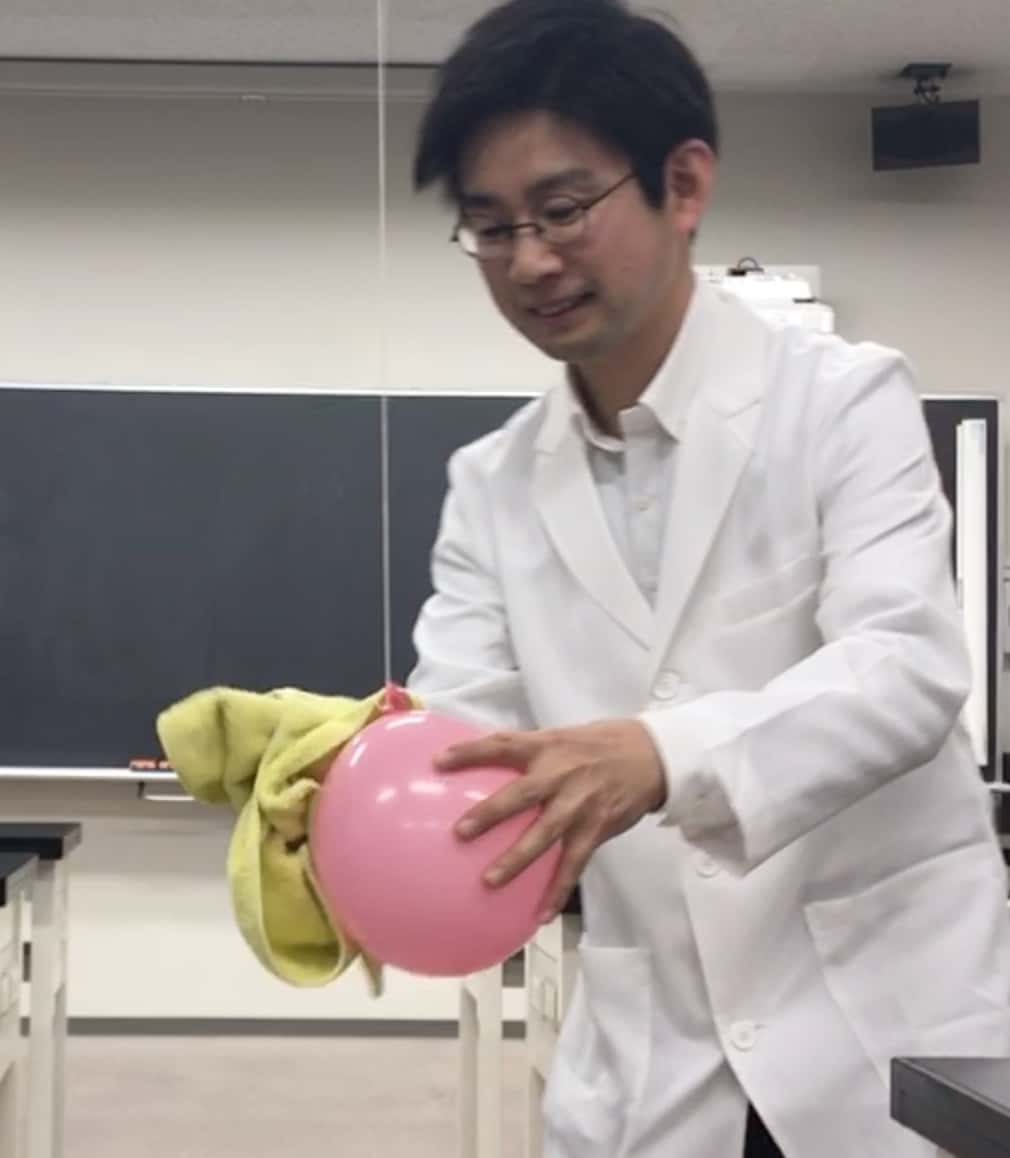

3 Rub the second balloon with the handkerchief in the same way, and slowly bring it close to the balloon hanging from the ceiling. What happens?
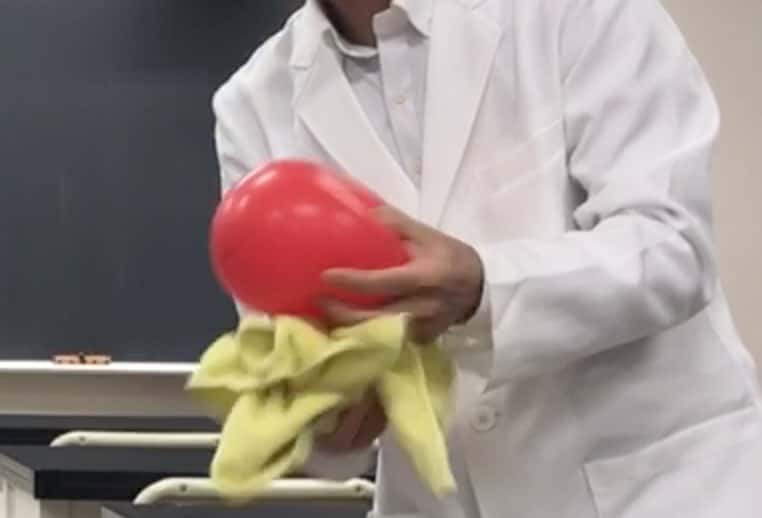

4 Next, bring the handkerchief (the one you used to rub the balloons) close to the hanging balloon. Is the reaction the same as before?
5 Finally, rub a balloon against your own clothes or hair, and then approach the hanging balloon. Something mysterious might happen!
Unraveling the Experiment’s Mechanism!
You should have observed some strange movements in the experiment—the balloons either running away or sticking together. The key to this phenomenon is the positive (+) and negative (-) charges that all matter possesses.
Normally, matter is electrically neutral because it has an equal amount of positive and negative charge. However, when you rub two different materials together, electrons (which carry a negative charge) can move from one object to the other. This is the true identity of static electricity.
Whether electrons are likely to move is determined by the type of material. The order of how easily materials become charged is shown in this chart, called the Triboelectric Series.

From my book, “Science Test Grade 3 & 4” (Kodansha, Ken Kuwako)
The further apart two materials are on this list, the more likely they are to generate static electricity when rubbed together. For example, when you rub a balloon (Rubber) with a handkerchief (let’s assume it’s Silk), electrons will move from the silk (on the right) to the rubber (on the left) in the Triboelectric Series.
As a result, the balloon gains many electrons and becomes negatively charged, while the handkerchief loses electrons and becomes positively charged.
Electricity follows a very important rule:
Charges of the same kind (negative & negative, positive & positive) repel (push away).
Charges of different kinds (positive & negative) attract (pull toward each other).
Now, keeping this rule in mind, let’s look at the results of our experiment…
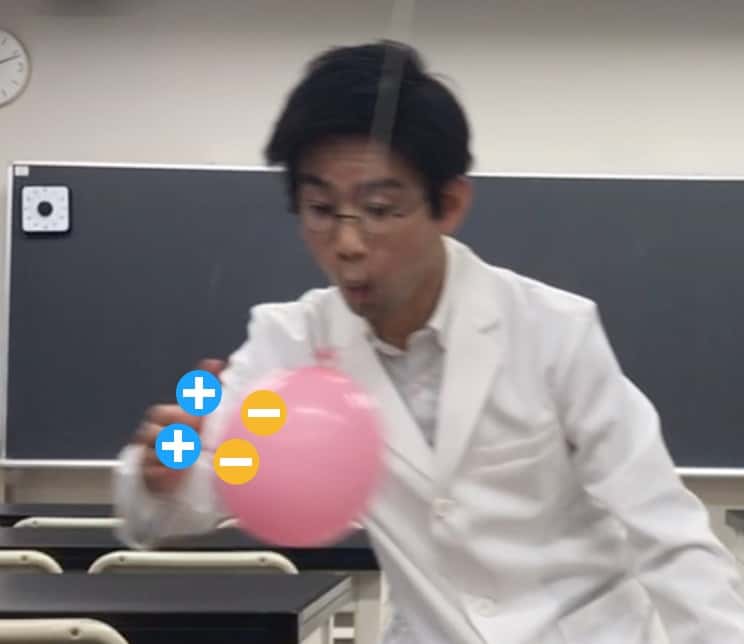
【Result 1】When you bring two rubbed balloons close together…
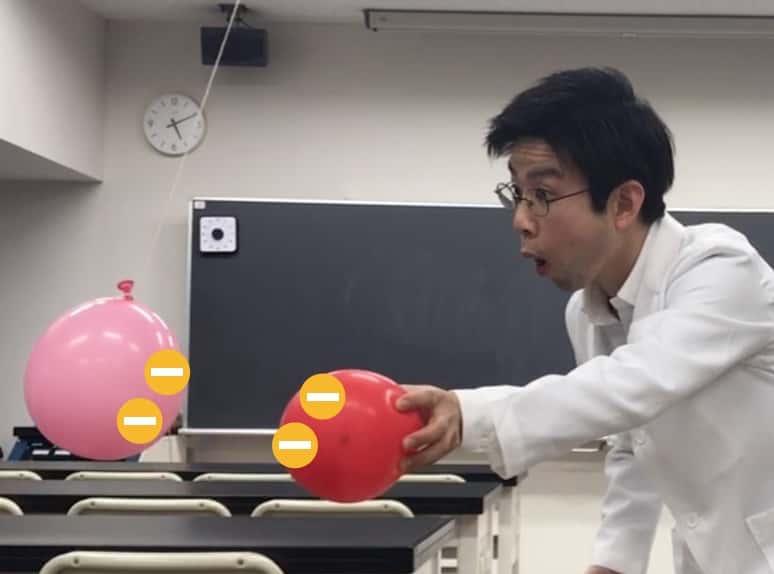

Since both balloons are negatively charged, they repel each other, essentially shouting, “Go away!” Isn’t it fascinating that a force can work without even touching?
【Result 2】When you bring the rubbed handkerchief close…
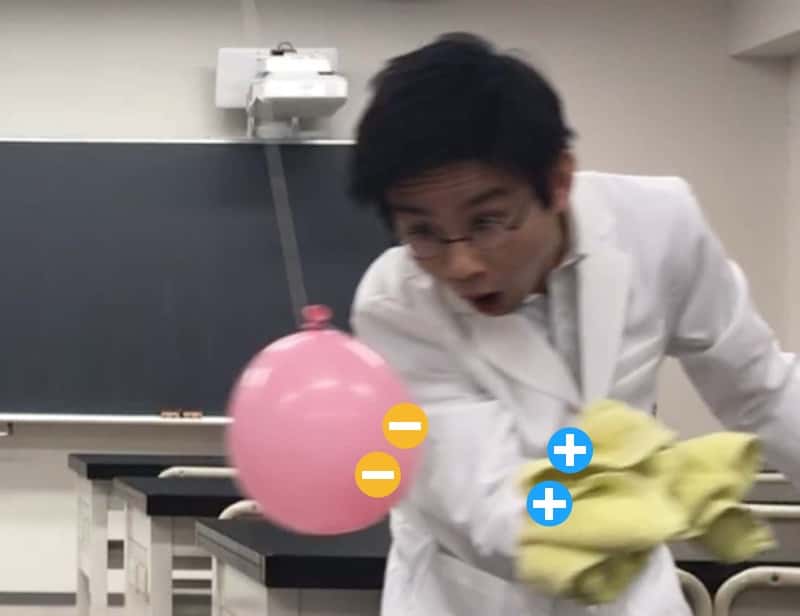

This time, you have the negative balloon and the positive handkerchief, so they attract each other, like saying, “I love you!”
【Result 3】When you bring yourself close to the balloon…
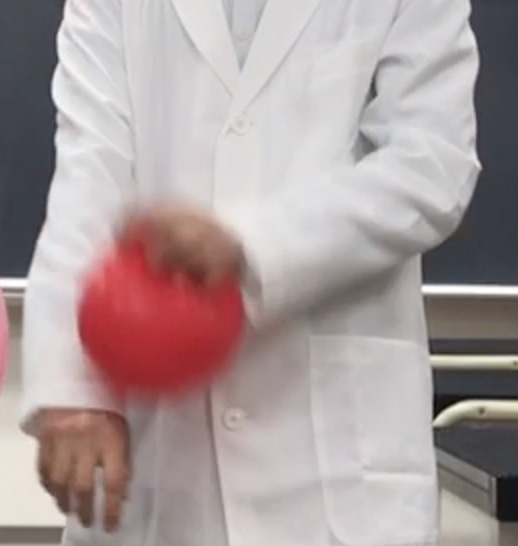


Astonishingly, you were also attracted to the balloon! This happens because when you rubbed the balloon on your body, electrons moved from your body to the balloon, making you positively charged. You become a human magnet! In this way, the invisible “migration of electrons” is what causes these seemingly magical phenomena.
See Even More Powerful Static Electricity!
“I want to see even stronger static electricity!” Fulfilling the dream of every science enthusiast is the Van de Graaff generator, a machine that creates static electricity. This incredible device can amplify the static electricity you see at home to lightning-level power!
We’ve also published videos of fun experiments using the Van de Graaff. These include experiments conducted on TV programs with many celebrities, such as Suzu Hirose, Ryohei Suzuki, Yasuko, and Osada and Matsuo from Chocolate Planet!

*Note: Experiments using a static electricity generator (Van de Graaff) are extremely dangerous and must only be conducted under the supervision of a professional. For requests regarding static electricity experiments (science classes, TV supervision/appearances, etc.), please contact us here.
【Special Feature】Static Electricity Experiments You Can’t Stop Doing!
Inquiries and Requests
Bringing the wonders and fun of science closer to you! This blog clearly summarizes enjoyable science experiments you can do at home, along with tips and tricks. Feel free to search around and explore!
The content of the Science Idea Notebook has been turned into a book. Find out more here
About the administrator, Ken Kuwako, click here
For various requests (writing, lectures, science classes, TV supervision/appearances, etc.), click here
Article updates are delivered on X!
![]() We post experiment videos on the Science Idea Channel!
We post experiment videos on the Science Idea Channel!
2月のイチオシ実験!梱包材で遊ぼう!
- 静電気の時期になってきました。子供と一緒に梱包材で盛り上がろう!→ やめられなくなる!静電気実験20
 体中に梱包材をはりつけてみよう!
体中に梱包材をはりつけてみよう!
テレビ番組等・科学監修等のお知らせ
- 「月曜から夜更かし」(日本テレビ)にて科学監修・出演しました。
書籍のお知らせ
- 1/27 『見えない力と遊ぼう!電気・磁石・熱の実験』(工学社)を執筆しました。
- サクセス15 2月号にて「浸透圧」に関する科学記事を執筆しました。
- 『大人のための高校物理復習帳』(講談社)…一般向けに日常の物理について公式を元に紐解きました。特設サイトでは実験を多数紹介しています。※増刷がかかり6刷となりました(2026/02/01)

- 『きめる!共通テスト 物理基礎 改訂版』(学研)… 高校物理の参考書です。イラストを多くしてイメージが持てるように描きました。授業についていけない、物理が苦手、そんな生徒におすすめです。特設サイトはこちら。

講師等・ショー・その他お知らせ
- 2/20(金)「生徒の進学希望実現支援事業」研究授業@福井県立若狭高等学校 講師
- 3/20(金) 日本理科教育学会オンライン全国大会2026「慣性の法則の概念形成を目指した探究的な学びの実践」について発表します。B会場 第3セッション: 学習指導・教材(中学校)③ 11:20-12:20
- 7/18(土) 教員向け実験講習会「ナリカカサイエンスアカデミー」の講師をします。お会いしましょう。
- 10/10(土) サイエンスショー予定
- 各種SNS X(Twitter)/instagram/Facebook/BlueSky/Threads
Explore
- 楽しい実験…お子さんと一緒に夢中になれるイチオシの科学実験を多数紹介しています。また、高校物理の理解を深めるための動画教材も用意しました。
- 理科の教材… 理科教師をバックアップ!授業の質を高め、準備を効率化するための選りすぐりの教材を紹介しています。
- Youtube…科学実験等の動画を配信しています。
- 科学ラジオ …科学トピックをほぼ毎日配信中!AI技術を駆使して作成した「耳で楽しむ科学」をお届けします。
- 講演 …全国各地で実験講習会・サイエンスショー等を行っています。
- About …「科学のネタ帳」のコンセプトや、運営者である桑子研のプロフィール・想いをまとめています。
- お問い合わせ …実験教室のご依頼、執筆・講演の相談、科学監修等はこちらのフォームからお寄せください。



