Cracking the Code: How ‘Magnetic Catch’ Powers Your Wireless Charger
I’m Ken Kuwako, a science trainer, and every day is an experiment.
Wireless phone chargers are incredibly convenient, aren’t they? No more fumbling with cables. But have you ever stopped to think about how they actually work? “How is electricity transmitted without a single wire connected?”
It feels like a technology straight out of a sci-fi movie. To uncover the secret of this “invisible power cable,” I bought a wireless charger and decided to take it apart! Inside, I found a key component that solved the mystery.
I’m sure you’ll have an “Aha!” moment and realize, “So that’s how it works!” Come, let’s embark on a journey of scientific discovery together!
Peeking Inside the Heart of a Wireless Charger
This is the wireless charger we’ll be dissecting today. It’s a very standard “just place it on” type.

First, I peeled off the non-slip rubber on the back… and there they were, the screw heads. I carefully removed them with a screwdriver.
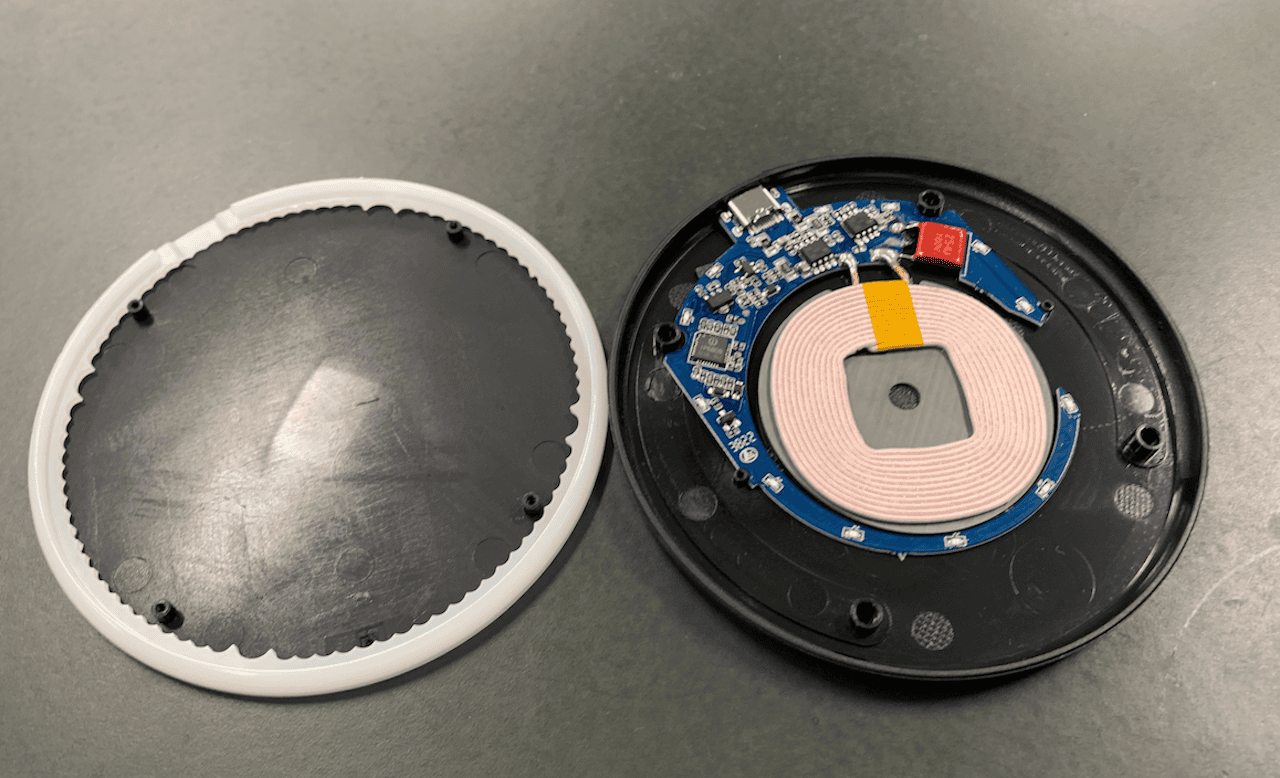
Then, I finally opened the case. Snap! Inside, I found a circuit board and, right in the center, a coiled-up copper wire. That’s right, a coil! This is the main star that makes the magic of wireless charging possible.
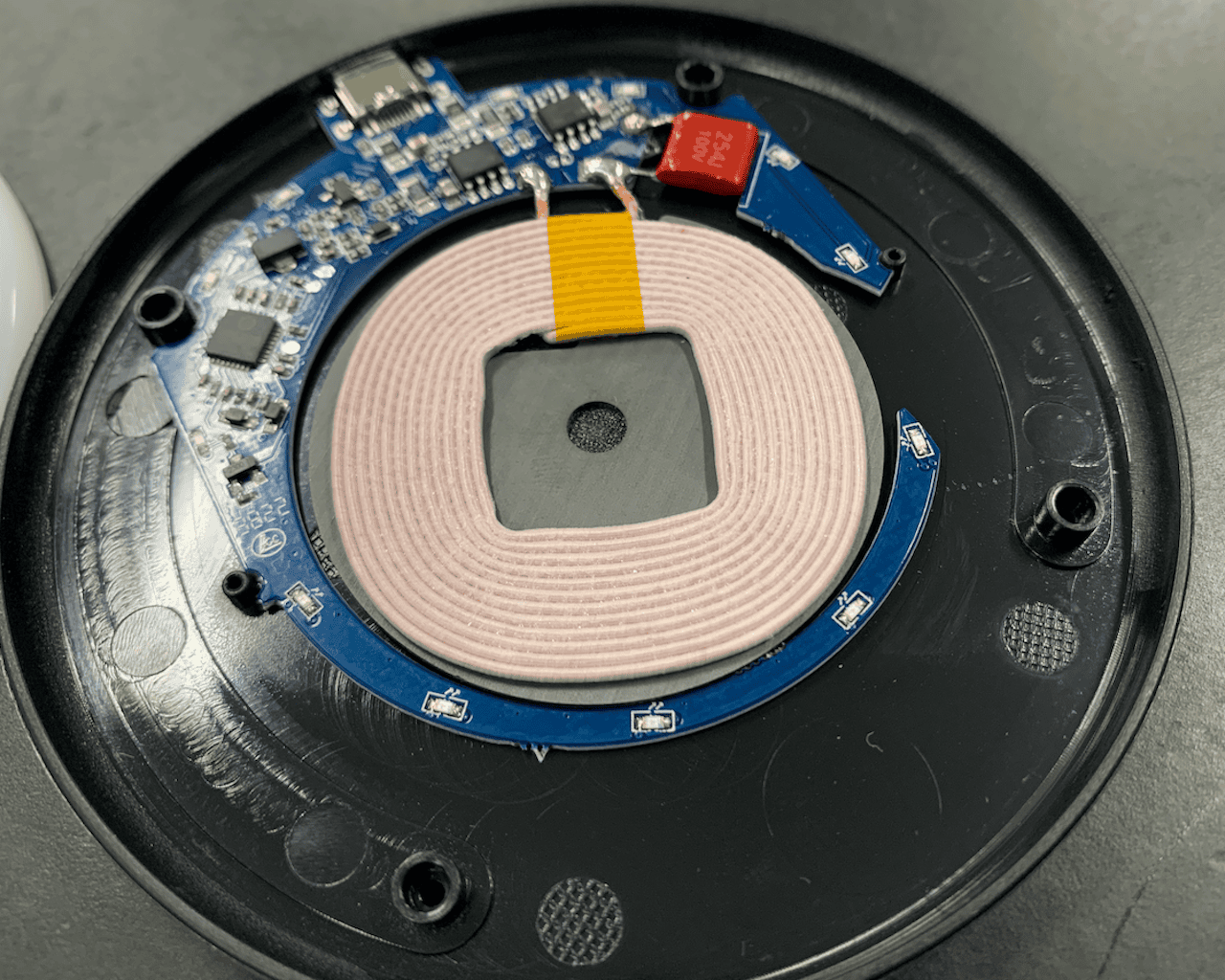
The Clue to the Mystery Was in the Instruction Manual!
So, how does this coil transmit electricity? The hint was surprisingly hidden in the safety warnings of the instruction manual.

Charging may not be possible in the following situations:
When used near a TV tower, power plant, or other locations that generate strong radio waves or noise. When the charging device is in contact with a card that has aluminum foil or other metal attached. When the charging device is covered by a metal smartphone case, etc.
Sanwa Supply Inc. (n.d.). Wireless Charger (700-WLC002) Instruction Manual. Retrieved June 12, 2024, from https://direct.sanwa.co.jp/contents/torisetsu/700-WLC002_m.pdf
From these warnings, we can see that wireless charging is a very delicate technology that relies on electromagnetism. It seems to have a particular aversion to metal. Why is that?
The Magic Is Actually ‘Magnetic Catch’
The mechanism behind wireless charging is an application of a phenomenon called electromagnetic induction, which you learn about in science class. It’s a principle discovered by the famous scientist Faraday, and simply put, it means “if you change the strength of a magnetic field, you can generate electricity in a coil.”
Wireless charging does this as follows:
The Transmitter (Charger): When electricity flows through the charger’s coil, it creates a changing magnetic field around it. Think of this as “throwing a ball.”
The Receiver (Smartphone): When you place your phone in that magnetic field, the coil inside your phone “catches” the changing magnetic field, and electromagnetic induction generates electricity. This is “catching the ball.”
That generated electricity then charges your battery. It’s exactly like a game of “magnetic catch” happening between the charger and your phone. The secret to transmitting power without a cable is the invisible force of magnetism.
The instruction manual’s warning about metal cases is because metal disrupts this game of magnetic catch. When metal is present, the magnetic field’s energy can be converted into heat instead of being properly received by the phone.
It Turns Out There’s a “Partner” in Your Phone Too!
“So, is there a coil inside my phone as well?” That’s right! Of course, I can’t dismantle my expensive phone, but let’s check out a famous teardown site for smartphones called “iFixit.”
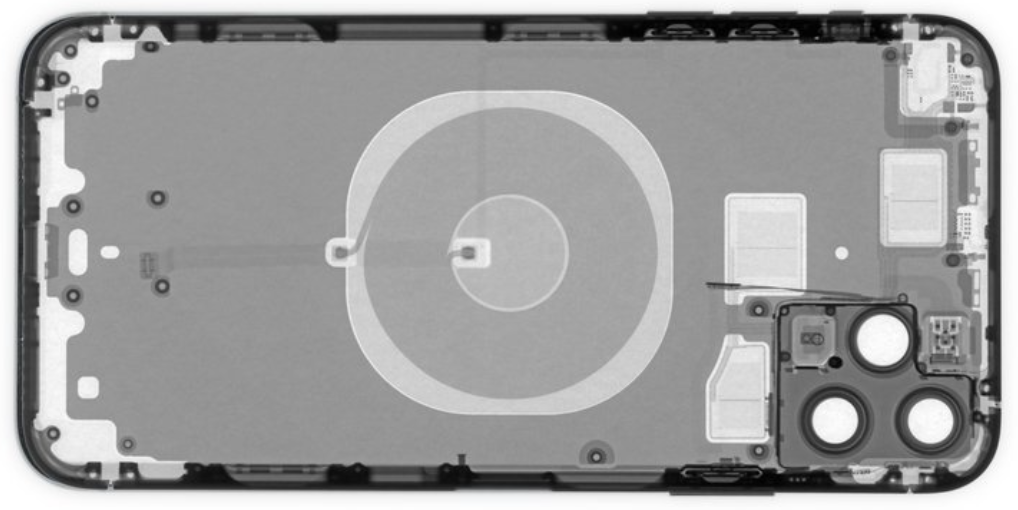
iFixit. (2019). iPhone 11 Pro Max Teardown. Retrieved June 12, 2024, from https://www.ifixit.com/Teardown/iPhone+11+Pro+Max+Teardown/126000
See? Just as you’d expect, there’s a coil perfectly matched to the one in the charger. These two coils must work as a pair for wireless charging to happen. The reason you have to place your phone “in the center” is the same as in a game of catch—if your partner is off-target, you can’t receive the ball.
This same principle is also used in IC cards like Suica. In the case of Suica, a brief burst of energy from the ticket gate is used to exchange information, while wireless charging continuously sends energy to charge a battery. It’s an interesting discovery that even though their purposes are different, their fundamental scientific principle is the same.
Be sure to check out our article where we opened up a Suica card:
By taking apart and looking inside the convenient technologies we use every day, we discover that they are filled with the wisdom of past innovators and the fundamental principles of science. There might be some “scientific magic” hidden around you as well.
Inquiries & Service Requests
We aim to make the wonders and fun of science more accessible! We’ve put together easy-to-understand explanations and tips for fun science experiments you can do at home. Please feel free to browse!
Learn more about the operator, Ken Kuwako, here.
For various requests (writing, lectures, science classes, TV supervision, appearances, etc.), please click here.
– We post updates on our articles on X!
![]() The Science Channel features experiment videos!
The Science Channel features experiment videos!