Is Your Intuition Wrong? A Deep Dive into Newton’s Third Law (with Mind-Twisting Examples!)
I’m Ken Kuwako, a science trainer. Every day is an experiment.
The Law of Action and Reaction: A Sumo Showdown Between an Elephant and a Gorilla!
Today, I want to pose a little “force” quiz. Imagine this: a massive elephant and a powerful gorilla face off in a sumo match. They collide with a “THUD!”, and the elephant pushes the gorilla back. Picture that scene in your mind.
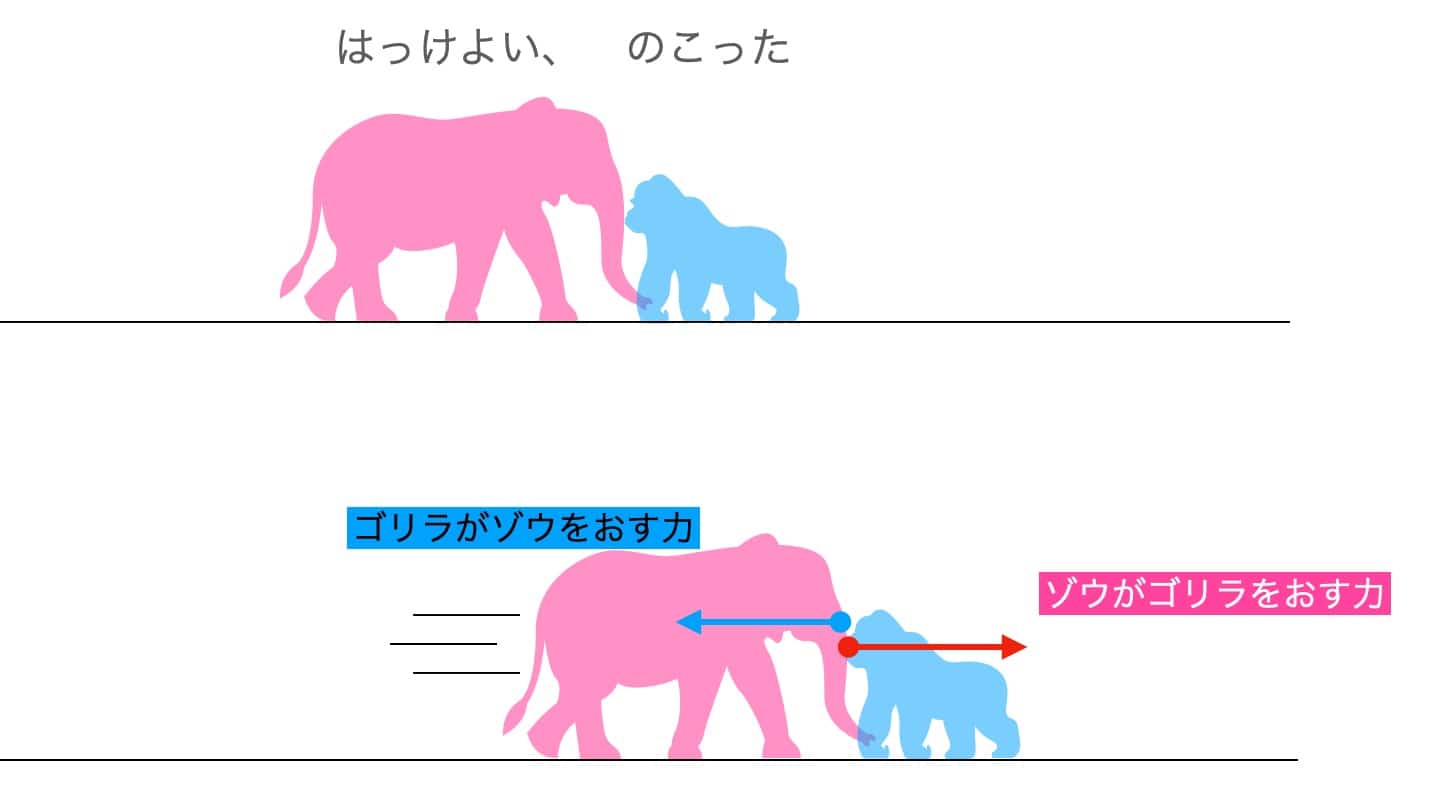
At this moment, which force is greater: the force the elephant exerts on the gorilla, or the force the gorilla exerts back on the elephant?
“Well, obviously the elephant is stronger, so the force it pushes with must be bigger, right?”
That’s the intuitive answer for many people, but wait! There’s a fascinating pitfall of physics hiding here that we often miss in our daily lives and that many people confuse. And that’s the topic for today: the Law of Action and Reaction.
What is the “Law of Action and Reaction”?
The surprising conclusion is that the force the elephant exerts on the gorilla and the force the gorilla exerts back on the elephant are always the exact same size!
Surprised? This is what’s known as Newton’s Third Law, or the Law of Action and Reaction.
The law is defined as follows:
“For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When object A exerts a force on object B, object B exerts a force on object A that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.”
Simply put, if you push something, it pushes back. If you pull something, it pulls back. When you push on a wall, the wall pushes back on you. And when the Earth’s gravity pulls on you, you’re pulling on the Earth with the exact same force (though with its immense mass, the Earth doesn’t budge!).
Let’s go back to our sumo match. The elephant applies a force as an “action” on the gorilla, and the gorilla applies an “equal and opposite reaction” force on the elephant.
So then why does the elephant move forward and the gorilla get pushed back?
“But wait, if the forces are equal, shouldn’t they both just stay still? The elephant actually moves forward and the gorilla gets pushed back, right?”
That’s an excellent question! This is where many people get confused, mixing up the Law of Action and Reaction with the equilibrium of forces.
- The Law of Action and Reaction describes a “pair of forces” acting between two different objects. The force from the elephant on the gorilla and the force from the gorilla on the elephant are a pair of action-reaction forces.
- The equilibrium of forces refers to a state where multiple forces acting on a single object cancel each other out, and the object’s state of motion doesn’t change (it’s either at rest or moving at a constant velocity).
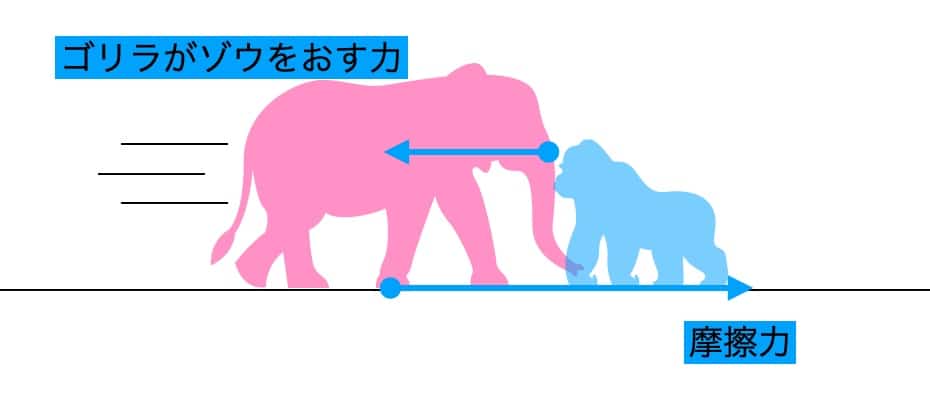
The reason the elephant moves forward is that the force acting on the elephant—the frictional force between the ground and the elephant’s feet—is greater than the force it receives from the gorilla. The elephant, with its large body and feet, can push strongly against the ground to generate a large frictional force, which allows it to overcome the reaction force from the gorilla and move forward.
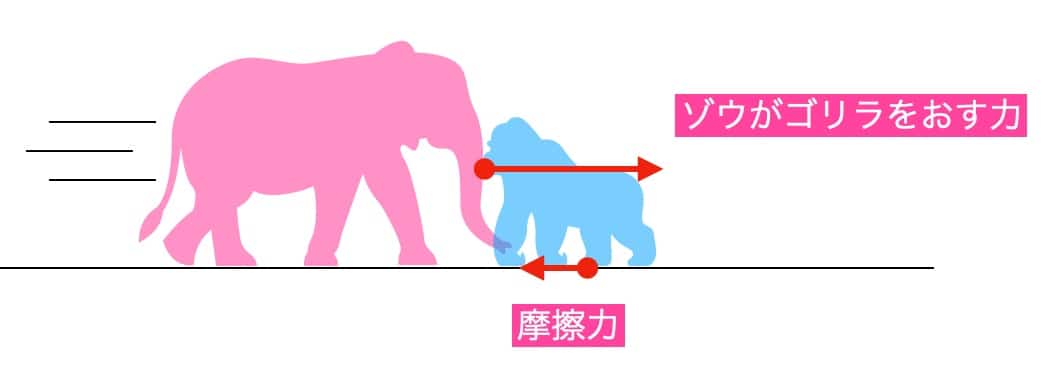
On the other hand, the gorilla is pushed backward because the frictional force between the ground and the gorilla’s feet is less than the force it receives from the elephant. The gorilla’s own friction isn’t enough to withstand the push from the elephant, so it gets pushed back as a result.
Action and Reaction in Everyday Life
The Law of Action and Reaction is all around us.
- Rocket Propulsion: The “action” of a rocket expelling hot gas backward generates a “reaction” force that pushes the rocket forward.
- Walking: The “action” of pushing the ground backward with your foot creates a “reaction” force from the ground that pushes you forward.
- Firing a Gun: The “action” of a gun firing a bullet forward creates a “reaction” force that causes the gun to recoil backward.
Pretty cool, right? It’s exciting to see how many physical laws are hidden in such ordinary, everyday phenomena.
The elephant and gorilla sumo problem is a great way to understand the concepts of the Law of Action and Reaction and the equilibrium of forces, which are fundamental yet profound in physics. I hope you’ll use what you’ve learned today to take a closer look at the “forces” at work around you!
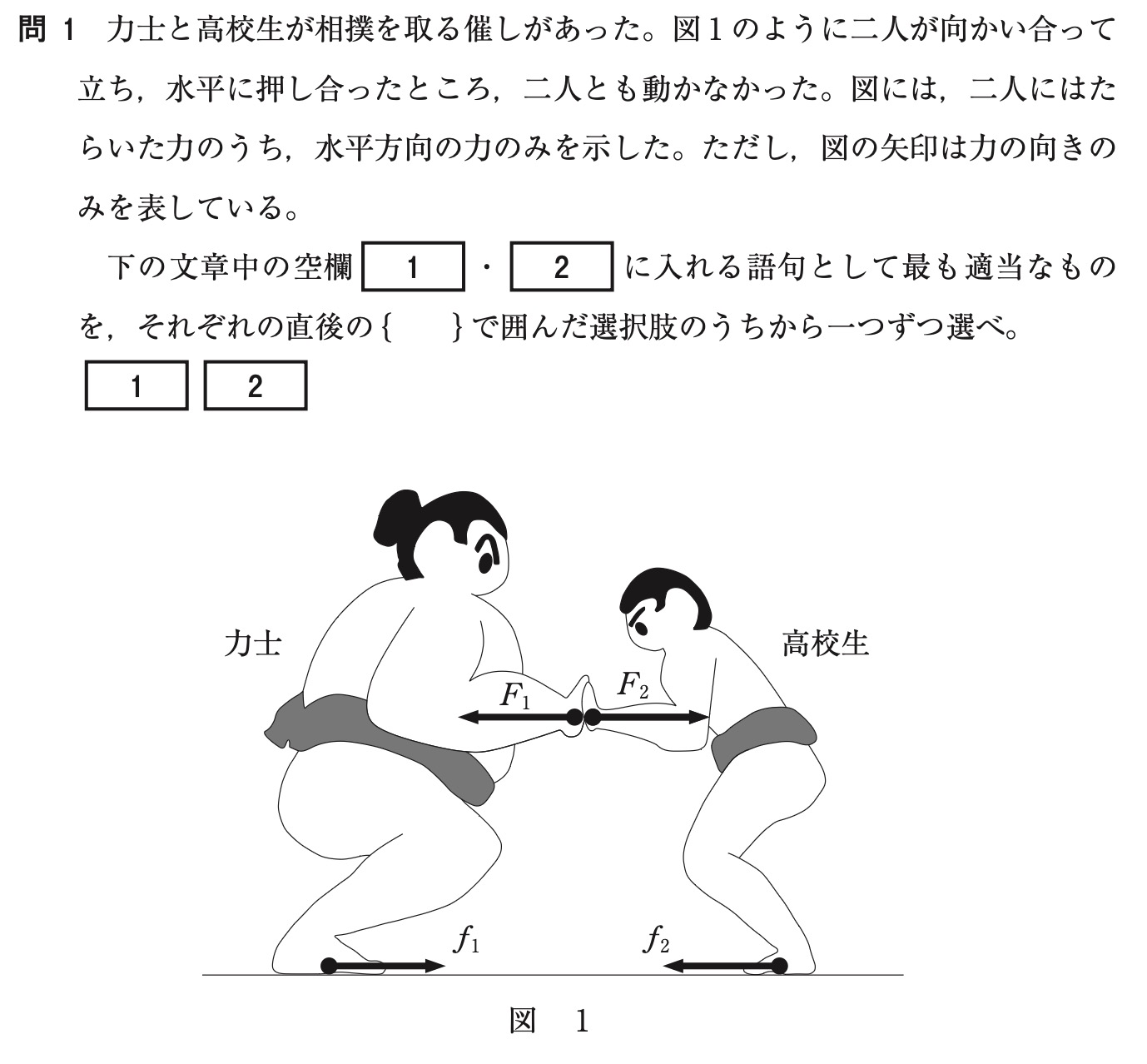
By the way, this exact type of question has appeared on Japan’s university entrance exams.

Contact and Requests
Want to get closer to the wonders and fun of science? We’ve compiled easy-to-understand tips and fun science experiments you can do at home. Feel free to search around!
・Learn about the creator, Ken Kuwako, here.
・For all requests (writing, lectures, science classes, TV supervision, appearances, etc.), please click here.
・Get updates on new articles on X!
![]() We post experiment videos on our Science Channel!
We post experiment videos on our Science Channel!
2月のイチオシ実験!梱包材で遊ぼう!
- 静電気の時期になってきました。子供と一緒に梱包材で盛り上がろう!→ やめられなくなる!静電気実験20
 体中に梱包材をはりつけてみよう!
体中に梱包材をはりつけてみよう!
テレビ番組等・科学監修等のお知らせ
- 「月曜から夜更かし」(日本テレビ)にて科学監修・出演しました。
書籍のお知らせ
- 1/27 『見えない力と遊ぼう!電気・磁石・熱の実験』(工学社)を執筆しました。
- サクセス15 2月号にて「浸透圧」に関する科学記事を執筆しました。
- 『大人のための高校物理復習帳』(講談社)…一般向けに日常の物理について公式を元に紐解きました。特設サイトでは実験を多数紹介しています。※増刷がかかり6刷となりました(2026/02/01)

- 『きめる!共通テスト 物理基礎 改訂版』(学研)… 高校物理の参考書です。イラストを多くしてイメージが持てるように描きました。授業についていけない、物理が苦手、そんな生徒におすすめです。特設サイトはこちら。

講師等・ショー・その他お知らせ
- 2/20(金)「生徒の進学希望実現支援事業」研究授業@福井県立若狭高等学校 講師
- 3/20(金) 日本理科教育学会オンライン全国大会2026「慣性の法則の概念形成を目指した探究的な学びの実践」について発表します。B会場 第3セッション: 学習指導・教材(中学校)③ 11:20-12:20
- 7/18(土) 教員向け実験講習会「ナリカカサイエンスアカデミー」の講師をします。お会いしましょう。
- 10/10(土) サイエンスショー予定
- 各種SNS X(Twitter)/instagram/Facebook/BlueSky/Threads
Explore
- 楽しい実験…お子さんと一緒に夢中になれるイチオシの科学実験を多数紹介しています。また、高校物理の理解を深めるための動画教材も用意しました。
- 理科の教材… 理科教師をバックアップ!授業の質を高め、準備を効率化するための選りすぐりの教材を紹介しています。
- Youtube…科学実験等の動画を配信しています。
- 科学ラジオ …科学トピックをほぼ毎日配信中!AI技術を駆使して作成した「耳で楽しむ科学」をお届けします。
- 講演 …全国各地で実験講習会・サイエンスショー等を行っています。
- About …「科学のネタ帳」のコンセプトや、運営者である桑子研のプロフィール・想いをまとめています。
- お問い合わせ …実験教室のご依頼、執筆・講演の相談、科学監修等はこちらのフォームからお寄せください。


